What is Denormalization?
- Definition:
Denormalization is the process of combining tables or adding redundant data to a database to make read queries faster, even if it means data might be repeated. - Why it happens:
In a normalized database (1NF, 2NF, 3NF), data is stored in separate tables to avoid redundancy.
But sometimes, joining many tables during queries slows down performance.
Denormalization helps reduce joins and speed up reading data. - Important:
Denormalization sacrifices storage space and may lead to redundancy but makes querying faster
Example:
Imagine you have a normalized database with these two tables:
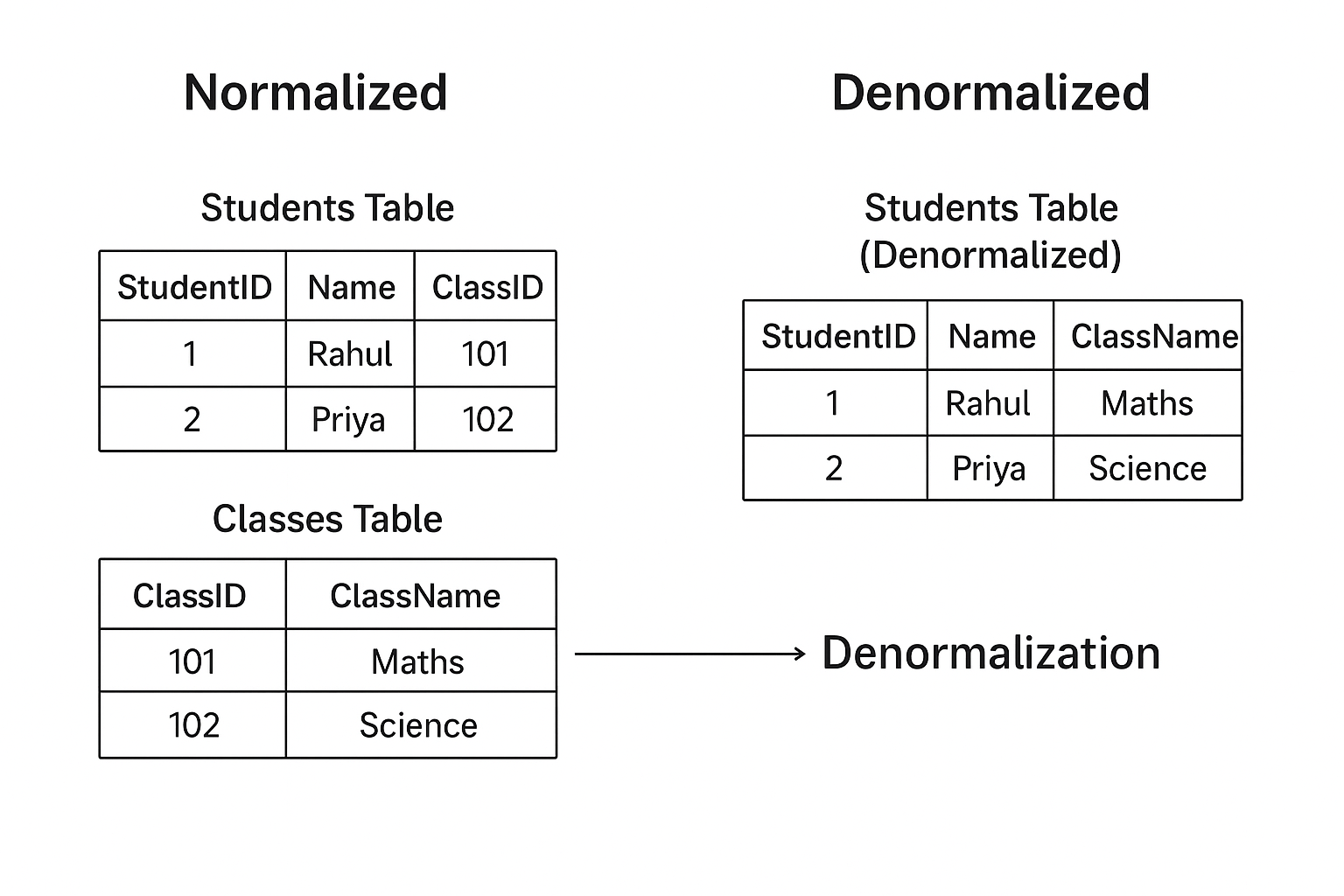
1. Students Table
| StudentID | Name | ClassID |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Rahul | 101 |
| 2 | Priya | 102 |
2. Classes Table
| ClassID | ClassName |
|---|---|
| 101 | Maths |
| 102 | Science |
his is normalized (no repeated data).
But if you want to show a list of students with their class name, you need a JOIN query:
sql
SELECT s.Name, c.ClassName
FROM Students s
JOIN Classes c ON s.ClassID = c.ClassID;
Denormalized version:
Instead of two tables, you combine them into one table like this:
| StudentID | Name | ClassID | ClassName |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Rahul | 101 | Maths |
| 2 | Priya | 102 | Science |
- Now, you don’t need JOINs to get student + class info.
- Queries are faster, but
ClassNameis repeated for every student in the same class.
Key Points
- Denormalization = less JOIN, more redundancy
- Helps read-heavy databases like reporting or analytics.
- Use carefully because it can cause data inconsistency if updates aren’t handled properly.
Normalized Database
Students Table
+-----------+-------+---------+
| StudentID | Name | ClassID |
+-----------+-------+---------+
| 1 | Rahul | 101 |
| 2 | Priya | 102 |
+-----------+-------+---------+
Classes Table
+---------+-----------+
| ClassID | ClassName |
+---------+-----------+
| 101 | Maths |
| 102 | Science |
+---------+-----------+
- No repeated data
- Need JOIN to get student + class info
sql
SELECT s.Name, c.ClassName
FROM Students s
JOIN Classes c ON s.ClassID = c.ClassID;
Denormalized Database
Students Table (Denormalized)
+-----------+-------+---------+-----------+
| StudentID | Name | ClassID | ClassName |
+-----------+-------+---------+-----------+
| 1 | Rahul | 101 | Maths |
| 2 | Priya | 102 | Science |
+-----------+-------+---------+-----------+
- No JOIN needed
- Query faster
- ClassName repeated → redundancy
sql
SELECT Name, ClassName
FROM Students;
Summary:
- Normalized = less redundancy, more JOINs
- Denormalized = more redundancy, fewer JOINs, faster reads