Aggregate = “Total / Summary”.
In SQL, aggregate functions are used to calculate values from multiple rows together (instead of checking each row one by one).
Example: In a class of students, instead of checking every student’s marks separately, we calculate total marks, average marks, highest marks, etc.
Common Aggregate Functions:
- SUM() → Adds values
- Example:
SUM(salary)= total salary of all employees. - Like: Total bill amount in a restaurant .
- Example:
- AVG() → Average value
- Example:
AVG(marks)= average marks of students. - Like: Average run rate in cricket .
- Example:
- COUNT() → Number of rows
- Example:
COUNT(student_id)= total students in class. - Like: Counting how many players are on the field.
- Example:
- MAX() → Highest value
- Example:
MAX(salary)= highest salary in company. - Like: Highest score in cricket match.
- Example:
- MIN() → Lowest value
- Example:
MIN(marks)= lowest marks in exam. - Like: Minimum bus ticket price.
- Example:
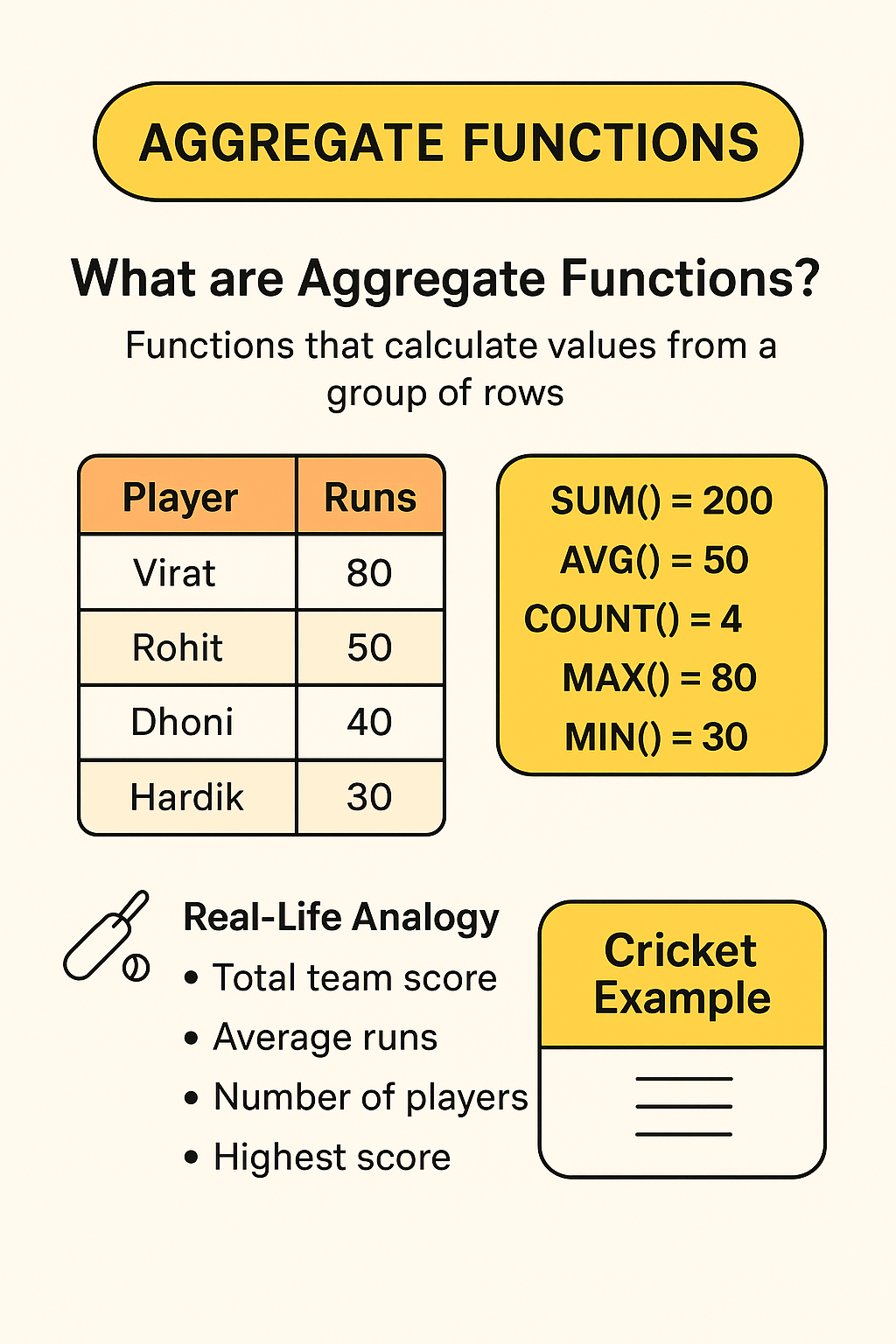
Real-Life Analogy (Cricket Example):
Imagine we have a scoreboard of players’ runs:
| Player | Runs |
|---|---|
| Virat | 80 |
| Rohit | 50 |
| Dhoni | 40 |
| Hardik | 30 |
SUM(runs)→ 200 (total team score)AVG(runs)→ 50 (average runs)COUNT(runs)→ 4 (number of players)MAX(runs)→ 80 (highest score)MIN(runs)→ 30 (lowest score)
Quick Recap for Freshers:
- Aggregate = Summary function.
- Works on group of rows, not single row.
- Used with
GROUP BYoften (like marks per subject, sales per city).